
There is practically no person who at least once in their life does not suffer from back pain in the lumbar region. This is how we pay for standing walking and our daily habits.
In addition to the damage that can affect the spine, its muscles, nerves and ligaments, it should be borne in mind that sometimes the back hurts in the lumbar region with internal diseases - diseases of the kidneys, gastrointestinal tract and female genital organs.
Symptoms of low back pain can range from dull to acute. The pain can go away on its own or become chronic (the symptom has been present for more than three months).
Dangerous! You should see a doctor immediately if:
- pain in the lumbar region arose abruptly after an obvious back injury;
- the temperature has risen sharply, there are vegetative disorders, loss of consciousness, sweating, breathing difficulties;
- involuntary emptying of the intestine and bladder occurs;
- there is numbness in the groin area;
- there was weakness of the lower limbs, their paresis or paralysis, reduced sensitivity;
- pains are given in the stomach and sharply increase when coughing or sneezing;
- the symptoms appeared against the background of severe weight loss, prolonged use of steroids, immunodeficiency;
- cases of cancer, inflammatory or degenerative diseases of the bone and cartilage tissue have been found in the family history.
Why does the back hurt in the lumbar region?
Myofascial pain
A muscle strain or spasm can develop gradually or occur suddenly. With a high load, the damage affects not only the muscle fibers, but also the ligament apparatus and fascia.
Muscle pain in the lower back appears after:
- lifting heavy weights or over-fatiguing at work or playing sports;
- playing sports from time to time. Muscles are especially vulnerable if you are inactive during the work week and then spend hours in the gym on weekends;
- a sharp increase in the weight of your own body, behind which the muscles do not have time to grow;
- prolonged sitting or standing in an uncomfortable position;
- daily carrying of a bag in one of the hands or over the shoulder;
- posture disorders. The spine performs its best support and protection function when not bent. Your lower back muscles experience the least stress when you sit with good support under your lower back and, in a standing position, distribute the weight evenly on both legs.
If the back hurts after a bruise, fracture, sprain, hypothermia, infectious disease, or known helminth invasion, myositis (inflammation) of the lower back muscles may be suspected. Severe pain is constantly present due to inflammation of muscle fibers, "nodules" are felt in the muscles - places of spasm. Inflammation can be acute or take a chronic form. With a long course of the disease, the pain is unstable, aggravated by prolonged lying or sitting, in the late afternoon or when the weather changes. Touching the muscles causes a sensation of pain and discomfort, the muscles of the lower back are in constant tension, an inflammatory edema is formed, the temperature rises locally and at the level of the whole organism.
With muscle spasm, the roots of the spinal nerves are violated, so the attacks often resemble an image of sciatica or sciatica: there are severe burning pains along the back of the thigh and lower leg, the limbs become numb, they lose sensation. The pronounced muscle tone in myositis causes the patient to take a forced position, walks and lies bent, moves on bent legs.
How to treat muscle pain in the spine? Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and analgesics are used to eliminate inflammation and pain. Medicines can be taken in the form of tablets, ointments, injections, transdermal patches with a gradual release of active ingredients. Irritating and warming ointments are also used, which reflexively increase blood flow to the muscles of the lower back. A larger volume of incoming blood contributes to washing out the products of inflammation and tissue breakdown.
The reduction of inflammatory edema is facilitated by injections of corticosteroids and vasoconstricting drugs.
If the cause of myositis is an infection or poisoning of the body with toxins from worms, then antibiotics or anthelmintic drugs are used initially. In this case, it is not possible to use warming ointments or compresses.
Spinal diseases involving nerve endings
In the lumbar region, the vertebrae are separated by elastic cartilaginous discs, which protect the spine from injury, but are themselves subject to wear and aging.
Normally, the disc is a gelatinous nucleus pulposus surrounded by a denser layer of the fibrous ring. The elasticity of the core is due to its ability to bind and hold water: when the load increases, water accumulates, and the elasticity increases, when the pressure decreases, the core releases water and becomes flatter.
Osteochondrosis in the vertebral region develops when the intervertebral discs are malnourished (their "drying") or with excessive local load. Most often, back pain is due to the fact that the lower poles of his intervertebral discs bear the greatest load when sitting, when lifting weights in front of them. At the same time, tears are formed, displacements in the discs, the vertebral ligaments are damaged, there is constant aching pain, throbbing.
Spine pain has several mechanisms of development:
- violation of microcirculation in the tissues surrounding the spine and, in particular, in the spinal canal, the formation of congestion and edema. Such conditions develop against the background of hypothermia, overheating, inflammatory processes.
- degenerative processes in the fixing ligaments of the spine. An increase in the mobility of the vertebrae leads to their slight non-physiological displacement and compression, which provokes the violation of nerves, blood vessels and the formation of hernias.
- axial compression of the vertebrae when lifting weights or damage to them during excessive rotation (turning).
- aseptic inflammation. The destruction of the nucleus leads to the release of sensitizing factors in the spinal canal. There is irritation of the nerve endings, which causes a spasm of the muscles that violate the neighboring vertebrae - above and below the hernia. Gradually, the reaction covers the entire lumbar region and leads to the fact that any movement causes a sensation of pain.
A weakened disc can rupture, causing the nucleus to bulge, bulge, or prolapse, and eventually a hernia. The appearance of a hernia puts pressure on the spinal cord and spinal nerve roots. In such conditions, sharp pain in the lower back appears sharply, diverging along the strangled nerve. The best known cases of compression of the sciatic nerve (sciatica), which are manifested by acute pain along the back of the thigh and lower leg, numbness of the limb from the side of the hernia, muscle weakness, involuntary bending of the legs.
Pain in the lumbar spine is aggravated in the sitting and standing position, when turning, tilts. Often there is a protective muscle reaction - a painful contraction of the muscles (roll formation) on both sides of the spine, which isolates the ward from unnecessary movements. Osteochondrosis subsequently leads to the appearance of sciatica (inflammation of the roots of the spinal nerves).
Radicular syndrome is dangerous when the nerves in the lower back, which are responsible for innervating internal organs (horns of the cauda equina), are pinched. At the same time, pain in the stomach is given, the function of the bladder and intestines is disturbed, there are problems with potency in men and gynecological diseases in women.
Many patients, due to the fact that the lower back hurts a lot, take analgesic positions: they deviate the body to the left, if the right side hurts, they are located on the right side. If the hernia is on the left. Characteristic is also the appearance of severe pain when pressing a hernia into the intervertebral space (symptom of humming).
How to treat if the back hurts with osteochondrosis:
- during a pain attack, you can take an anesthetic pose: lie on your back and put a roller under your knees. It is also advisable to sleep on a hard surface;
- from analgesic drugs, NSAIDs can be taken orally or as injections on both sides of the spine in the lumbar hotel;
- use local irritants as a distraction therapy: mustard plasters, iodine mesh, pepper patch and ointments;
- eliminate myotic spasm through manual therapy, acupuncture, vacuum massage, reflexology, gymnastics;
- during the attenuation of the acute period, mud, ozokerite, heating can be used.
Treatment of pain in radicular syndrome includes:
- provision of bed rest, lumbar traction (dry or under water);
- the use of novocaine blocks in the place of infringement, the use of NSAIDs or weak opiates;
- physiotherapy - stimulation of the microcurrent, electrophoresis with analgesics.
Indications for surgery are constant acute pain, as well as impaired function of internal organs, the development of paralysis of the limbs, seizure of a hernia in the spinal canal.
Degenerative inflammatory lesions
Spondyloarthrosis (inflammation of the joint facets of the vertebrae) occurs with degeneration, a decrease in the height and volume of the intervertebral discs. Pain in the lower back appears from excessive stretching of the capsule and increased pressure on the surface of the intervertebral joints. The pain causes the patient to bend more in the lower back, thereby increasing the overload of the intervertebral joints. Especially the discomfort in the lower back is aggravated by wearing shoes with heels, walking for a long time, getting off the elephants, positions in which the body deviates backwards, for example when looking at something above the head.
In patients with this diagnosis, stiffness in the lower back is noted in the morning, pain increases during the day or after exercise. It has a widespread character and it is difficult to clearly show the boundaries: discomfort is determined in the gluteal muscles, groin region, lower abdomen and scrotum in men. This spondyloarthrosis differs from radicular syndrome when it is possible to locate the source of the pain.
What to do to relieve the pain? It usually helps to take a supine position, bending the legs at the hip and knee joints.
Their drugs are preferred non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and non-narcotic analgesics.
Muscle relaxants are also added as they relieve muscle tension and improve spinal mobility.
Psychotherapy has a positive effect, as chronic pain introduces the patient to a state of depression.
Spondylosis, unlike osteochondrosis, mostly affects the fibrous ring of the intervertebral disc and the anterior longitudinal ligaments. With this disease, calcification of connective tissue structures occurs with the formation of growths along the edge of the vertebrae - osteophytes. These formations cause a violation of microcirculation near the nerve roots and lead to the fact that the back hurts in the lower back, and the mobility of this department is also limited.
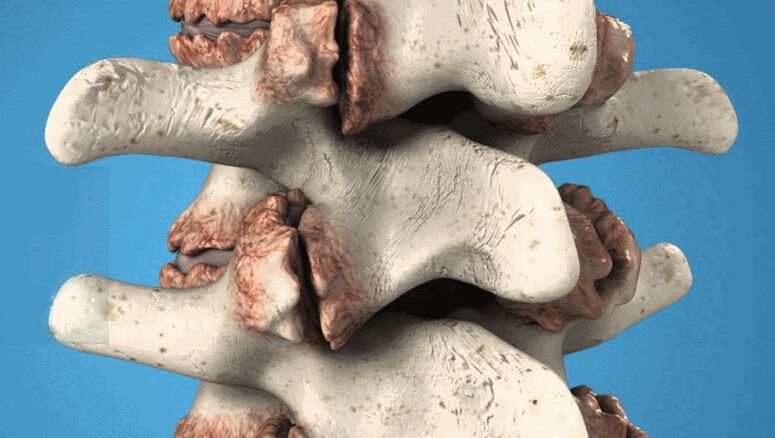
Vertebral osteophytes are pathological growths that damage nerves and blood vessels.
Treatment is usually conservative, with the use of anti-inflammatory drugs, analgesics, vitamins. A good effect is given by electrophoresis with novocaine, lidase, manual therapy, physiotherapy (amplipulse, laser installation, shock wave therapy to destroy compacted elements and increase spinal mobility).
Note! In the advanced stage, the osteophytes do not resolve. Although their size is small, treatment is aimed at eliminating inflammation, pain, improving metabolism. If the back doesn't hurt much, then nothing is done with the growths. If the osteophytes are causing persistent pain or are large in size, they can be removed during surgery.
Diseases of a tumor nature
Low back pain can occur from compression of the spinal cord by a tumor from the outside (extramedullary formations) and from the inside (intramedullary, originating from the cerebrospinal substance itself).
Cells of various tissues can grow pathologically:
- fat - a lipoma is formed;
- nerve roots - neuroma;
- vessels of the spinal cord - hemangioma;
- auxiliary tissue - glioma;
- bone tissue - osteosarcoma;
- cartilage - chondrosarcoma.
The tumor process, especially malignant, is characterized by a painful syndrome resembling sciatica (it can be one-sided and bilateral), a general deterioration of the patient's condition and exhaustion.
If the pathology affects the area of the lumbar vertebrae I-IV, then there is a burning pain in front and on the sides of the upper thigh, incomplete paralysis of this area.
With a lesion in the region of the lumbar IV - II sacral segments, numbness of the paragenital region, impaired motor and sensory innervation of the gluteal muscles, posterior incontinence of the thigh, calf, stool and urinary tract are noted.
A pronounced disturbance in the functioning of the pelvic organs occurs with a neoplasm in the region of the V-III sacral vertebrae. The patient suffers from sexual impotence or menstrual disturbances, constipation or fecal and urinary incontinence.
Cancer treatment is specific, pain relievers and anticancer drugs are prescription drugs.
As you can see, low back pain is usually caused by musculoskeletal conditions. They can be diagnosed by clinical signs and research data, the main task of which is to correctly determine the nature of the disease and not to confuse it with oncological causes, diseases of internal organs or trauma. If you experience lower back pain, we recommend that you always seek the advice of a neurologist or orthopedist.
















































